Break the loops which rule you
How AI can change your addiction behaviour
What exactly is addiction
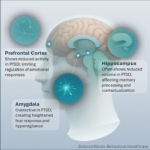
Addiction is a state of compulsive behaviour where the person cannot help but do the thing of his addiction (e.g. drinking). It arises from complex interactions between genetics, environment, and repeated exposure to a rewarding stimulus—whether a drug like opioids or alcohol, or an activity like gambling. These stimuli trigger intense surges of dopamine in the brain’s reward circuit, particularly the nucleus accumbens, creating powerful associations between the substance/behaviour and pleasure or relief.
Over time, neuroplastic changes diminish the brain’s natural reward sensitivity and impair prefrontal cortex functions responsible for self-control, decision-making, and impulse regulation. Tolerance develops, requiring larger doses or more frequent engagement to achieve the same effect, while withdrawal produces physical and psychological distress that further drives use.
Types of Addiction
- Substance Addiction: They include disorders involving the use of substances such as alcohol, drugs, and nicotine.
- Behavioural Addiction: Other impulsive and compulsive related disorders. For example, compulsive gambling or sexual behaviour.
What begins as voluntary choice gradually becomes a hijacked system where craving overrides reason. Addiction is not a moral failing but a medical condition that alters brain structure and function, often requiring comprehensive treatment combining behavioural therapy, medication, and social support to restore balance and enable recovery.
What do the studies tell us about integrating AI
Early Detection & Risk Prediction AI scans patterns from smartphone sensors, social media activity, wearable devices (heart rate, sleep, movement), and medical records to flag early warning signs of addiction—often months before a person or doctor notices a problem.
Remote Monitoring for Clinicians Doctors receive dashboards showing daily adherence, mood trends, and risk scores, allowing them to intervene quickly without waiting for the next appointment.
Relapse Prediction Machine learning models achieve 80–90% accuracy in predicting relapse days or weeks in advance by combining biometric data, mood logs, location history, and past relapse triggers.

24/7 AI Chatbots & Virtual Support Apps like Woebot, Tess, or custom recovery bots deliver instant cognitive behavioral therapy, craving management techniques, and emergency de-escalation whenever the user needs it.
Drawbacks of Traditional Methods for Treating Addiction

Stigma and Fear of Judgment
Many people avoid seeking help due to shame or social stigma. Traditional, in-person treatment can feel intimidating, causing delays in seeking support or dropping out early.
One-Size-Fits-All Treatment Plans
Most traditional approaches follow fixed protocols (e.g., standard CBT routines, fixed rehab structures) that don’t adapt dynamically to individual triggers, relapse patterns, or emotional cycles.
Limited Monitoring Between Sessions
Therapists usually interact with patients only during scheduled appointments. Cravings, urges, and relapses often occur between sessions, leaving large gaps without support.
Which tools you can use to combat addiction
Sober Grid: A peer-support social network designed for people in recovery from substance use disorders. It lets users connect with nearby sober peers, post updates, use a “burning desire” alert when cravings hit, and access 24/7 peer-coaching. It also uses AI/ML behind the scenes to analyse user behaviour and flag people at higher risk of relapse.
Replika: An AI chatbot companion app where users create an avatar and chat with a generative-AI that adapts to their conversation style. Though not addiction-specific, it supports emotional expression, mood-tracking and offers a non-judgmental outlet—useful in recovery contexts for loneliness or emotional triggers.
Mindwell AI: A mental-wellness app that combines mood tracking, journaling and AI-driven counselling/insights. It focuses on identifying emotional patterns, stress or relapse risk factors and giving early prompts or interventions. While not solely focused on substance-addiction, its features align with relapse-prevention models. Eage
OpenRecovery– is an AI-powered addiction-support app featuring “Kai,” a 24/7 conversational assistant that provides personalised guidance, coping tools, and non-judgmental support. It offers multiple recovery pathways—including 12-Step, CBT-based tools, and mindfulness—so users can choose what fits them best.
OpenRecovery is a digital addiction-support platform that uses AI-powered behavioural guidance, personalized recommendations, and real-time conversation support to help individuals manage cravings, track progress, and stay engaged in recovery.

1. AI-Based Recovery Assistant (Kai)
OpenRecovery features an AI conversational assistant called Kai, designed to offer:
- 24/7 emotional support
- Non-judgmental conversations during cravings
- Practical tips and motivational messages
- Guidance through different recovery stages (early recovery, relapse prevention, long-term lifestyle change)
2. Personalized Recovery Pathways
The AI system analyses:
- User check-ins
- Mood logs
- Craving reports
- Daily habits
3. AI-Driven Trigger & Pattern Identification
The app tracks user behaviors over time, helping identify:
- When cravings typically occur
- Emotional states that lead to relapse
- Social or environmental triggers
- Times when motivation is lowest
4. Just-In-Time Support Interventions
Based on user behaviour and patterns, the AI sends timely prompts such as:
- Motivational nudges
- Coping strategy reminders
- Breathing exercises
- Relapse-prevention tools
Takeaway
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally transforming addiction care by directly overcoming the fatal flaws of traditional approaches. Where stigma once kept millions silent, AI delivers anonymous, 24/7 support through chatbots and apps—no judgment, no waiting. Where one-size-fits-all protocols failed to account for individual triggers and biology, machine-learning systems now adapt therapy, dosage, and interventions in real time. Where clinicians were blind between appointments, they now receive daily dashboards of mood, sleep, cravings, and risk scores, enabling intervention days or weeks before relapse—with predictive models reaching 80–90% accuracy.
These tools do not replace human connection; they extend it, making evidence-based help accessible exactly when and where it is needed most. By closing the gaps of silence, rigidity, and invisibility that have long undermined recovery, AI is turning addiction treatment from reactive and generic to proactive, personalized, and always available. With responsible implementation, it offers credible hope: fewer overdoses, lower relapse rates, and millions of lives reclaimed.