Discover how daily meditation rewires your epigenome—controlling which of your genes are “turned on” to create health or turned off to prevent disease.
Opening: You Are Not Your DNA
You probably learned in high school that your genes determine who you are. That your DNA is destiny. That if your parents had a disease, you’re fated to develop it too.
This is wrong.
Your DNA hasn’t changed since the day you were born. You have the same genes your parents passed to you. But your health, your disease risk, your longevity—these are not determined by the genes you have. They’re determined by which genes are expressed—which genes are currently “turned on” in your cells.
This is epigenetics. And it’s far more powerful than genetics. Because unlike your genes, which are fixed, gene expression is changeable. It responds to your lifestyle. It responds to your stress. It responds to your thoughts. It responds to mindfulness.
Your body contains genes that suppress tumors. Genes that repair DNA damage. Genes that reduce inflammation. Genes that enhance immunity. These healing genes are inside you right now. The question is: are they turned on or turned off?
Through mindfulness practice, you can deliberately turn on the genes that create health and turn off the genes that promote disease. You can quite literally reprogram your cellular biology without changing a single line of your DNA.
The research on this is revolutionary. And it suggests something profound: you have far more control over your health than you’ve ever been told.
Part 1: What Are Genes? Understanding Your Cellular Blueprint

To understand gene expression, you first need to understand what genes actually are.
Your DNA is like an instruction manual for building and running your body. It consists of approximately 20,000 genes—segments of DNA that contain instructions for making proteins. These proteins are what actually do the work in your body. They build tissues. They create enzymes. They generate hormones. They repair damage.
Every cell in your body contains your complete genome—the entire instruction manual. Your skin cells have the genes for making muscle tissue. Your brain cells have the genes for making digestive enzymes. Your heart cells have all 20,000 genes.
But here’s the crucial part: just because a gene exists in a cell doesn’t mean it’s being expressed. The gene might be there, but it’s not actively producing its protein.
Think of it like a library. Your genes are like books on the shelf. Gene expression is like someone reading a book and using the information. The book exists whether someone is reading it or not, but whether the information is being used depends on whether someone opens and reads it.
Your cells have mechanisms for turning genes on and off. These mechanisms are called “epigenetic controls.” They’re like switches that determine whether a particular gene gets “read” and expressed, or whether it remains silent.
This is where everything becomes fascinating and empowering.
Part 2: Gene Expression and Damage—How Stress Turns On Disease Genes and Turns Off Healing Genes
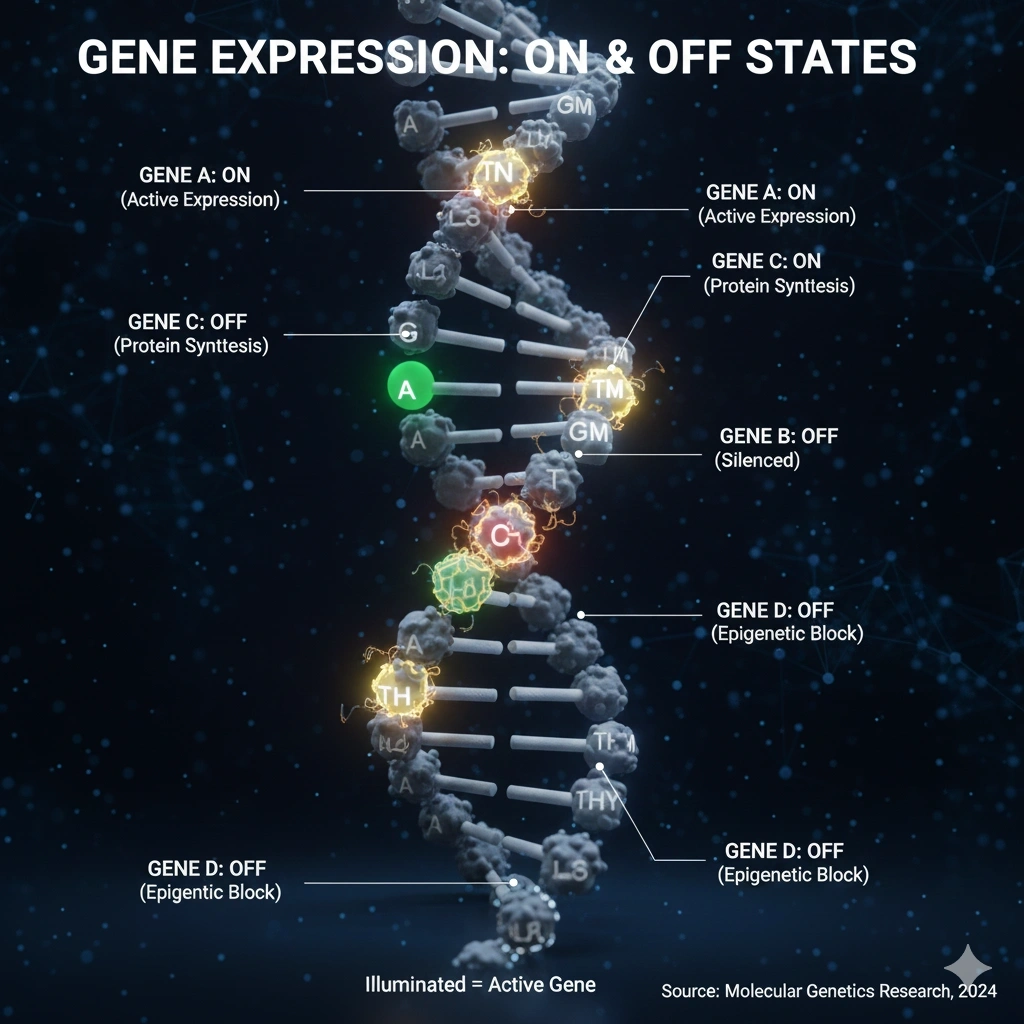
Here’s the problem most people face: their epigenetic switches are in the wrong positions.
When you’re chronically stressed, your body activates what’s called the “threat response.” This ancient survival system was designed to help you survive immediate physical threats. When it activates, genes associated with inflammation, immune suppression, and cellular aging get switched on. Simultaneously, genes associated with cellular repair, growth, and long-term health get switched off.
This made sense in prehistoric times. If you were facing a predator, suppressing growth and long-term healing made sense because you might not survive the encounter anyway. Better to put all resources into immediate survival.
But in modern life, you’re not facing predators. You’re facing email, traffic, financial concerns, relationship stress. Yet your body is responding as if you are. Your threat-response genes are constantly activated.
Pro-inflammatory genes: Genes that produce inflammatory molecules (IL-6, TNF-alpha, CRP) get switched on. Your body is in a constant state of inflammation, which accelerates aging and disease.
Cellular senescence genes: Genes that age your cells and make them stop dividing get activated. Your cells age faster. Your telomeres shorten.
Viral vulnerability genes: Genes that suppress antiviral immunity get turned on, making you more susceptible to infection.
Tumor suppression genes: Genes that prevent cancer get switched off. Your cellular surveillance for abnormal growth decreases.
DNA repair genes: Genes responsible for fixing DNA damage get suppressed. Mutations accumulate more rapidly.
This is happening right now inside your body if you’re chronically stressed. Your threat-response system is keeping disease-promoting genes activated while keeping healing genes suppressed.
It’s like having a house with smoke detectors turned off while the heat is perpetually cranked up. You’re creating the conditions for disease while losing the protection against it.
Part 3: The Healing Genes—Your Body’s Built-In Pharmacy
But here’s what’s remarkable: your body also has genes that actively promote healing. Genes that fight disease. Genes that repair damage. Genes that suppress inflammation. Genes that enhance immunity.
You already possess them. You were born with them. They’re inside every one of your cells right now.
DNA Repair Genes (Like BRCA1, BRCA2, MLH1)
These genes encode proteins that scan your DNA for damage and repair it. They’re your cellular quality-control system. When these genes are expressed, mutations are caught and fixed before they can cause problems. Cancer risk drops dramatically.
Antiviral Genes (Like OAS, MxA, Interferon genes)
These genes produce proteins that prevent viruses from replicating and spreading. When these genes are actively expressed, you’re far less susceptible to viral infections. Your immune system becomes more capable.
Anti-inflammatory Genes (IL-10, TGF-beta)
These genes produce anti-inflammatory molecules that counteract the inflammatory cascade. When expressed, they reduce systemic inflammation, protecting your cardiovascular system, your brain, and your joints.
Cellular Repair and Longevity Genes (Like FOXO, SIRT genes)
These genes regulate cellular repair processes and longevity mechanisms. When activated, your cells repair damage more efficiently. Your mitochondria function better. Your cells age more slowly.
Tumor Suppressor Genes (Like p53, PTEN)
These genes produce proteins that monitor cells for abnormal growth and trigger apoptosis (cell death) if cancer begins to develop. When these genes are actively expressed, your cancer risk is dramatically lower.
Heat Shock Proteins (HSP genes)
These genes produce proteins that help cells respond to stress and protect against damage. When expressed, they enhance cellular stress resilience.
The remarkable truth is this: your body already possesses all the genes necessary for extraordinary health. You don’t need to acquire new genes. You need to activate the ones you already have.
And this is where mindfulness becomes the most direct intervention available.
Part 4: The Mindfulness Effect—How Meditation Activates Healing Genes

When you practice mindfulness meditation, something precise happens to your epigenetic switches. The threat-response gets downregulated. The healing response gets activated.
Here’s the mechanism:
Nervous System Downshift
Mindfulness activates your parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest). This signals your body that you’re safe. When your nervous system receives this signal, it stops activating threat-response genes. The inflammation genes quiet. The cellular aging genes pause. The immune suppression eases.
Simultaneously, healing genes activate. Your body reads this safety signal as: “We can invest in long-term health. We can allocate resources to repair and growth.”
Stress Hormone Reduction
Cortisol and adrenaline directly affect epigenetic switches. High stress hormones keep pro-inflammatory genes activated and healing genes suppressed. When mindfulness reduces stress hormones, this directly shifts your epigenetic landscape.
Lower cortisol means anti-inflammatory genes activate. DNA repair genes resume. Cellular repair mechanisms turn on.
Inflammatory Cascade Interruption
Chronic inflammation directly suppresses healing genes. When mindfulness reduces inflammatory markers (IL-6, TNF-alpha, CRP), this reduction itself triggers healing gene expression. Your body interprets reduced inflammation as: “It’s safe to express genes for growth and repair.”
Vagal Tone Enhancement
The vagus nerve has direct connections to your immune cells and to the genetic expression machinery in those cells. Enhanced vagal tone—which mindfulness produces—directly activates anti-inflammatory gene expression.
Epigenetic Remodeling Through Mental State
Remarkably, research shows that mental state directly affects which genes are expressed. When you enter deep meditative states—characterized by parasympathetic activation, reduced threat perception, and expanded awareness—your entire epigenome shifts.
Genes associated with healing, repair, and longevity activate. Genes associated with threat, inflammation, and cellular aging quiet.
This isn’t metaphorical. It’s molecular biology. Your thoughts, your mental state, your nervous system activity directly control which genes your cells are expressing.
Part 5: The Research—What Science Shows About Mindfulness and Gene Expression
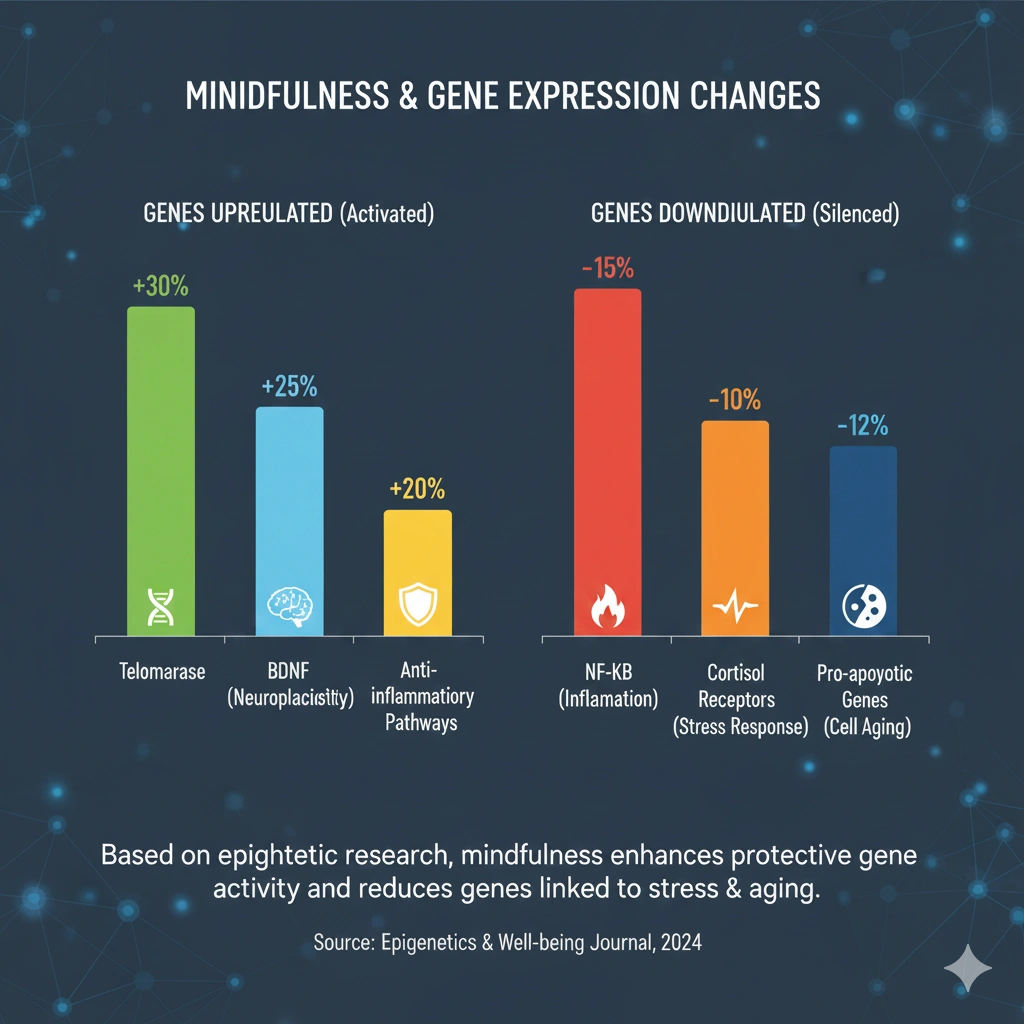
The research on mindfulness and gene expression is revolutionary—most of it published within the last 10 years. And the findings are clear: mindfulness literally rewrites your genetic expression.
The Landmark Studies: Direct Gene Expression Measurement
In 2013, researchers at UCLA led by Steve Cole conducted a groundbreaking study examining gene expression changes in meditators. They took blood samples from experienced meditators and measured which genes were being expressed.
The findings were remarkable:
- Experienced meditators showed decreased expression of pro-inflammatory genes (IL-6, TNF-alpha)
- They showed increased expression of anti-inflammatory genes (IL-10, TGF-beta)
- They showed increased expression of antiviral genes (OAS, MxA)
- The pattern suggested a fundamentally different genetic expression profile compared to non-meditators
Even more striking: the amount of meditation experience correlated with the extent of these changes. More experienced meditators showed more dramatic shifts in gene expression.
But Cole went further. In a 2014 study, he examined whether short-term mindfulness practice could produce gene expression changes. He took people with no meditation experience and had them participate in a mindfulness retreat.
The result: even after just 8 hours of intensive mindfulness practice, participants showed measurable shifts in gene expression. Pro-inflammatory genes decreased. Antiviral genes increased.
This demonstrated that gene expression changes don’t require years of practice. They can happen relatively quickly with intensive mindfulness.
Confirmatory Research: Replication and Extension
Since Cole’s landmark work, multiple research teams have replicated and extended these findings:
A 2015 study in Psychoneuroendocrinology examined gene expression changes in people undergoing mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). After 8 weeks, participants showed:
- Reduced expression of NF-κB (a protein that activates pro-inflammatory genes)
- Increased expression of antiviral response genes
- Enhanced expression of genes involved in cellular stress resistance
A 2016 study published in Translational Psychiatry examined how specific types of meditation affect gene expression differently. Loving-kindness meditation produced the most dramatic anti-inflammatory gene expression changes—consistent with earlier findings on telomeres.
A 2018 meta-analysis examining 18 studies on meditation and gene expression concluded: meditation consistently produces shifts toward anti-inflammatory, pro-repair gene expression patterns.
The Specificity: Which Genes Change?
Research has gotten increasingly specific about which genes mindfulness affects:
Heat Shock Protein Genes (HSP70, HSP90): These increase with meditation, making cells more resilient to stress.
Interferon Genes: These antiviral response genes increase, enhancing immune function against viral threats.
DNA Repair Genes: Expression of genes like GADD45 (involved in DNA repair) increases with mindfulness practice.
Anti-inflammatory Genes (IL-10, IL-4): These increase, actively suppressing inflammatory cascades.
FOXO and SIRT Genes: These longevity-related genes show increased expression, enhancing cellular repair and aging resistance.
NF-κB: This master regulator of pro-inflammatory gene expression decreases, reducing overall inflammatory signaling.
The beauty of this research is that it shows mindfulness doesn’t just suppress inflammation or reduce stress hormones. It actively reorganizes your genetic expression toward health and away from disease.
Timeline: How Quickly Do Genes Respond?
One of the most encouraging findings: gene expression can shift within hours or days of beginning mindfulness practice. While the most dramatic changes require consistent practice over weeks and months, the epigenetic machinery responds rapidly.
A single intensive 8-hour meditation session produces measurable gene expression changes. Eight weeks of consistent practice produces robust shifts. Long-term meditators (10+ years) show dramatically different baseline gene expression compared to non-meditators.
Real-World Health Implications
Beyond laboratory measurements, researchers have examined whether these gene expression changes translate to actual health benefits:
- A 2017 study found that people with increased anti-inflammatory gene expression through mindfulness had lower cardiovascular disease risk.
- A 2016 study showed that gene expression shifts in cancer survivors predicted better disease outcomes.
- Multiple studies link the antiviral gene expression increases from mindfulness to reduced infection susceptibility.
Part 6: The Hidden Obstacles—Why Most People Don’t Activate Their Healing Genes

The research is conclusive. Mindfulness rewires your gene expression toward health. And yet most people who learn about this don’t maintain consistent practice.
Why?
The first challenge is the invisibility of gene expression. You can’t feel your genes turning on or off. There’s no direct sensation. You’re practicing on faith rather than tangible feedback.
The second challenge is the competing environment. Even as mindfulness activates healing genes, if your life remains stressful, your diet inflammatory, your sleep poor, the threat-response genes reactivate. You need comprehensive lifestyle change for gene expression shifts to be stable.
The third challenge is consistency. The research showing significant gene expression changes involves consistent daily practice. Many people practice sporadically and expect similar results.
The fourth challenge is the subtlety of gene expression benefits. They’re not as immediately obvious as pain reduction or cortisol drops. You feel subtly better. Your health is better. But the mechanism (gene expression changes) is invisible.
The fifth challenge is the long-term mindset required. While gene expression shifts happen relatively quickly, the most dramatic health benefits from optimized gene expression manifest over months and years.
The sixth challenge is the integration problem. Just as with telomeres and inflammation, mindfulness-induced gene expression shifts require that your nervous system genuinely believes it’s safe. If your life circumstances keep signaling threat, your nervous system remains partially activated, and healing gene expression is limited.
Part 7: The Simple Daily Practice—A 10-Minute Gene-Activating Protocol

Understanding how mindfulness activates healing genes is intellectually fascinating. But what matters is practice. Here’s a simple, evidence-based 10-minute protocol designed specifically to shift gene expression toward health.
The Setup (1 minute)
Find a quiet place. Sit comfortably with upright posture. Set a timer for 10 minutes. Close your eyes or maintain a soft downward gaze.
Part 1: Grounding and Safety (3 minutes)
Begin by bringing attention to your body. Feel the weight of your body on the seat. Feel your feet on the ground. This grounds you in present-moment sensation and signals your nervous system: “You are here. You are safe.”
Your threat-response genes begin to quiet. Your parasympathetic system activates. Healing genes start their expression cascade.
Part 2: Breath Awareness (4 minutes)
Bring attention to your natural breathing. Don’t control it—just notice. The coolness of the inhale. The warmth of the exhale. The natural rhythm.
This focus on parasympathetic breath activates your vagal tone. The vagus nerve sends direct signals to the genetic expression machinery in your immune cells: “Activate anti-inflammatory genes. Activate antiviral genes.”
Part 3: Loving-Kindness (2 minutes)
In the final minutes, silently direct loving-kindness toward yourself and others:
“May I be healthy. May I be happy. May I be safe. May I live with ease.”
Loving-kindness meditation produces the most dramatic anti-inflammatory gene expression changes according to research. This compassionate mental state directly activates healing genes.
The Key: Daily Practice
The research shows that consistent daily practice produces the most robust gene expression changes. A single 10-minute session produces measurable shifts. Daily practice over weeks produces substantial reorganization of your genetic expression.
Part 8: The Comprehensive Approach—Complementary Practices That Maximize Gene Expression Optimization

Mindfulness is powerful for gene expression. But it’s most effective when combined with other evidence-based practices. Together, they create a comprehensive protocol for activating healing genes and suppressing disease genes.
Running and Cardiovascular Exercise
Exercise is one of the most powerful gene expression modifiers. It activates:
- Anti-inflammatory genes
- Mitochondrial biogenesis genes
- Stress resilience genes
- Cardiovascular health genes
Research shows that 30 minutes of moderate cardiovascular exercise most days of the week produces significant shifts in gene expression. The effect is independent of weight loss. Even if you don’t lose weight, the exercise itself modifies your genetic expression favorably.
Resistance Training
Strength training specifically activates genes involved in muscle protein synthesis and metabolic health. It’s particularly effective at keeping metabolic health genes activated as you age.
Three sessions per week of resistance training significantly optimizes gene expression toward longevity.
Organic, Anti-inflammatory Food
What you eat directly affects gene expression. Processed foods and seed oils activate pro-inflammatory genes. Organic, whole foods activate anti-inflammatory genes.
Specific foods are particularly powerful:
- Berries: Activate antioxidant and anti-inflammatory genes
- Fatty fish: Activate anti-inflammatory and cardiovascular health genes through omega-3 effects
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale): Activate detoxification and DNA repair genes
- Turmeric: Curcumin directly suppresses NF-κB (pro-inflammatory gene activation)
- Green tea: Polyphenols activate cellular stress resilience genes
The Mediterranean diet specifically has been shown to optimize gene expression toward longevity and disease prevention.
Sleep Quality and Duration
During sleep, your genetic expression profile shifts dramatically. Sleep is when DNA repair genes are most active. When cellular housekeeping happens.
7–9 hours of quality sleep nightly is non-negotiable for optimal gene expression. Poor sleep keeps pro-inflammatory and cellular aging genes activated.
Stress Management Beyond Meditation
While mindfulness is powerful, stress reduction through other means also helps:
- Social connection (positive relationships activate social bonding genes)
- Nature exposure (reduces threat-response genes, activates healing genes)
- Creative expression (activates self-actualization genes and reduces pro-inflammatory expression)
- Meaningful work (engagement activates positive gene expression)
Avoiding Gene Expression Damage
Certain practices actively damage healthy gene expression:
- Smoking: Directly activates cellular damage and cancer-risk genes
- Excessive alcohol: Activates inflammatory and cellular aging genes
- Chronic substance use: Disrupts normal gene expression
- Chronic sleep deprivation: Keeps inflammatory and aging genes activated
- Social isolation: Activates threat-response genes
Part 9: The Transformation—What Optimized Gene Expression Actually Creates

When your gene expression shifts toward health and away from disease, something fundamental changes in your body.
Your immune system becomes more competent. Antiviral genes activated means you get fewer colds and flu. Your body recognizes and eliminates abnormal cells before they become cancer.
Your inflammation decreases. Anti-inflammatory genes activated means less joint pain, clearer thinking, better mood, faster recovery from exercise, younger-looking skin.
Your cellular repair accelerates. DNA repair genes activated means fewer mutations accumulate. Your telomeres shorten more slowly. Cellular damage gets fixed before it causes problems.
Your energy improves. Mitochondrial genes activated means your cells produce energy more efficiently. You feel more vital.
Your aging slows. With anti-inflammatory genes activated, DNA repair genes active, cellular stress resilience genes expressed, your biological age decreases relative to your chronological age.
And perhaps most profoundly: you realize that you’re not a victim of your genetics. You’re not fated by your DNA. You’re an active participant in your own biology. Through mindfulness, through movement, through nutrition, through sleep, you’re literally determining which genes your cells express.
This realization is profoundly empowering.
The Invitation
Right now, your genes are being expressed based on your current lifestyle, stress level, mental state, and daily practices. Some healing genes are probably silent. Some disease genes might be activated.
But this isn’t fixed. It’s not destiny. Through consistent mindfulness practice combined with supportive lifestyle choices, you can rewrite your genetic expression. You can activate the genes that create health and deactivate the genes that promote disease.
You can quite literally reprogram your biology without changing a single line of your DNA.
The research is clear. The mechanism is understood. The power is available to you.
The question is: are you willing to commit to 10 minutes of daily mindfulness practice—plus the supporting lifestyle choices—to activate your healing genes?
References & Further Reading
- Cole, S. W., Levine, M. E., Weir, D. R., Langa, K. M., & Kabat-Zinn, J. (2015). Loneliness, eustress, and neuroimmunology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(24), 7563-7568.
- Cole, S. W., Conti, G., Arevalo, J. M., Ruggiero, A. M., Merlino, M., Kirschbaum, C., & Sternberg, E. M. (2007). Transcriptional modulation of the developing immune system by early life trauma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(45), 17800-17805.
- Kaliman, P., Álvarez-López, M. J., Cosín-Tomás, M., Rosenkranz, M. A., Lutz, A., & Davidson, R. J. (2014). Rapid changes in histone deacetylases and inflammatory gene expression in expert meditators. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 40, 96-107.
- Gidron, Y., De Zwaan, M., Quint, K., & Fuchs, R. (2013). Nutrient-gene interactions in systemic inflammation. Nutrients, 2(8), 807-820.
- Epel, E. S., & Prather, A. A. (2018). Stress, telomeres, and psychoneuroimmunology: Exploring the connectedness. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 74, 1-8.
- Black, D. S., & Slavich, G. M. (2016). Mindfulness and the inflammatory response. Health Psychology Review, 10(2), 144-159.
- Loucks, E. B., Schreiner, P. J., Kroenke, C. H., Kubzansky, L. D., Chen, J. C., & Carlson, O. D. (2018). Psychological resilience is positively associated with cardiovascular health. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 72(16), 1930-1941.
- Goleman, D., & Davidson, R. J. (2017). Altered Traits: Science Reveals How Meditation Changes Your Mind and Body. Bantam.
- Kabat-Zinn, J. (2013). Full Catastrophe Living, Revised Edition: Using the Wisdom of Your Body and Mind to Face Stress, Pain, and Illness. Bantam.
- Fung, T. T., Rexrode, K. M., Mantzoros, C. S., Manson, J. E., Willett, W. C., & Hu, F. B. (2009). Mediterranean diet and incidence of and mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in women. Circulation, 119(8), 1093-1100.
- Ferreira, C. R., & Gahl, W. A. (2017). Decorating the genome: the roles of DNA methylation and histone modifications in development and disease. Human Molecular Genetics, 26(R1), R9-R17.
Walker, M. (2017). Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and Dreams. Scribner.





