From faster diagnoses to robot-assisted surgeries, the adoption of AI in healthcare is advancing medical treatment and patient experiences.

Artificial intelligence is transforming healthcare by simplifying the lives of patients, doctors, and hospital administrators. It performs tasks typically done by humans but in less time and at a lower cost. Moreover, AI in healthcare appears in various ways. For example, it finds new links between genetic codes, powers surgery-assisting robots, and automates administrative tasks. It also personalizes treatment options and more. Consequently, AI enhances efficiency while enabling more precise and personalized care.
What Is AI in Healthcare?
AI in healthcare involves using machine learning, natural language processing, deep learning, and other technologies to improve the experiences of healthcare professionals and patients. These AI tools help health professionals manage resources more effectively. They also allow for a more proactive approach to various aspects of healthcare. As a result, doctors can make quicker, more accurate diagnoses. Additionally, health administrators can find electronic health records faster, while patients receive timely and personalized treatments. Overall, AI is transforming the healthcare industry.

Examples of AI in Healthcare
To help you better understand this rapidly evolving field, we’ve rounded up some examples and use cases of AI in healthcare.
AI in Medical Diagnosis
Every year, about 400,000 hospitalized patients suffer preventable harm, resulting in 100,000 deaths. Given this, AI’s potential to improve diagnostics is one of its most exciting healthcare applications. Incomplete medical histories and large caseloads often lead to deadly human errors. However, AI is immune to these variables. It can predict and diagnose diseases faster than most medical professionals, reducing the risk of error. Consequently, AI offers a promising solution to enhance patient safety and care.
AI in Drug Discovery
The drug development industry is burdened by rising costs and research that demands thousands of human hours. Each drug’s clinical trials cost an estimated $1.3 billion, yet only 10% of those drugs reach the market. However, AI is speeding up this process due to technological breakthroughs. It helps design drugs, predicts side effects, and identifies ideal candidates for clinical trials. As a result, AI is making drug development more efficient and cost-effective.
AI in Patient Experience
AI can support digital communications by offering schedule reminders, tailored health tips, and suggested next steps to patients. Additionally, AI improves the speed and accuracy of health diagnoses, which enhances patient visits. Consequently, this leads to faster and more personalized care. Furthermore, by providing a seamless patient experience, AI allows hospitals, clinics, and physicians to treat more patients each day.
AI in Healthcare Data Management
Highly valuable information can sometimes get lost among trillions of data points. Additionally, the inability to connect important data slows drug development, preventative medicine, and accurate diagnosis. However, AI can handle massive volumes of data efficiently. It breaks down data silos and connects information in minutes, which previously took years to process. As a result, AI reduces the time and costs of healthcare administrative processes. Consequently, this leads to more efficient daily operations and improved patient experiences.
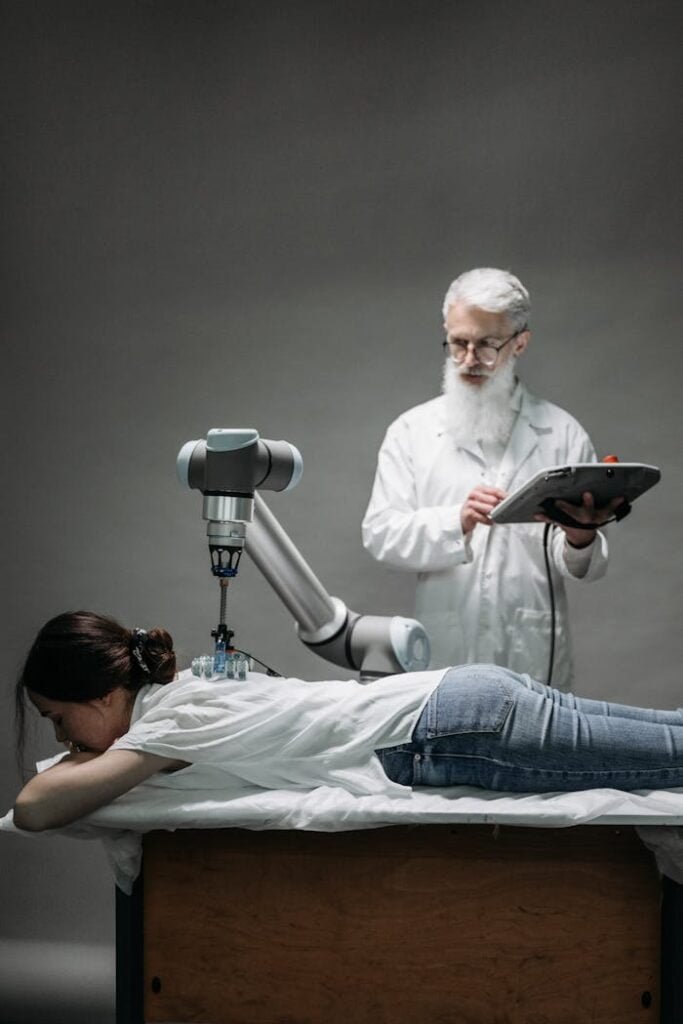
AI in Robotic Surgery
Hospitals use AI and robots for tasks ranging from minimally invasive procedures to open heart surgery. Surgeons control a robot’s mechanical arms from a computer console. Meanwhile, the robot provides a three-dimensional, magnified view of the surgical site. The surgeon leads the team, who works closely with the robot throughout the operation. Consequently, robot-assisted surgeries result in fewer complications, less pain, and quicker recovery times.

Future and potential of AI in the healthcare ecosystem
AI offers opportunities to reduce human error, assist medical professionals, and provide patient services 24/7. As AI tools develop, they could further enhance reading medical images, X-rays, and scans, diagnosing issues, and creating treatment plans.
AI applications also help streamline various tasks, from answering phones to analyzing population health trends. For example, future AI tools might automate or support more clinical and staff work. Consequently, this would allow humans to focus more on effective and compassionate face-to-face care.
We believe AI will play a crucial role in the future of healthcare. Machine learning, a key component of AI, drives the development of precision medicine, which is a much-needed advance in care. Although early attempts at providing diagnoses and treatment recommendations have been challenging, we expect AI to excel in these areas eventually. Additionally, rapid advances in AI for imaging analysis suggest that machines will soon examine most radiology and pathology images. Furthermore, speech and text recognition are already used for patient communication and capturing clinical notes. Their usage is expected to increase.

Conclusion
The integration of AI in healthcare has the potential to revolutionize patient care and outcomes. AI-driven predictive analytics can improve the accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of disease diagnosis and lab testing. Additionally, AI aids in managing population health and establishing guidelines by providing real-time information and optimizing medication choices. AI’s use in virtual and mental health support also shows promise. However, addressing issues such as bias and lack of personalization is crucial for effective and equitable AI use.
To implement AI effectively, several measures are needed. First, develop and enforce cybersecurity strategies to protect patient data and healthcare operations. Collaboration among healthcare organizations, AI researchers, and regulatory bodies is essential for setting guidelines and standards for AI algorithms. Investing in research and development will advance AI technologies tailored to healthcare challenges.
AI can analyze population demographics and disease prevalence to identify patients at higher risk for certain conditions, aiding in prevention or treatment. Edge analytics can detect irregularities and predict healthcare events, ensuring resources like vaccines are distributed where needed.
Public perception of AI varies. While people are open to using AI for health purposes, they prefer human practitioners for complex issues. Building trust and educating patients are crucial for successful AI integration. Overcoming challenges like data quality, privacy, and bias is essential.
Collaboration among stakeholders is vital for developing robust AI systems and ethical guidelines. Continued research and innovation will unlock AI’s full potential in healthcare, leading to improved patient outcomes, greater efficiency, and better access to personalized treatment.