Prompt engineering requires better understanding of Language models. Language modules serve as the backbone of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, empowering them to comprehend, analyze, and produce human language with remarkable proficiency. Often known as natural language processing (NLP) components, these modules are essential in a wide array of AI applications, ranging from chatbots and virtual assistants to machine translation and sentiment analysis. Their pivotal role transforms the way we interact with technology, bridging the gap between human communication and machine understanding.
Recap
In the previous module, we learnt about the basics of prompt engineering, explored whether it’s an art or science, who prompt engineers are, and the role they play in the AI ecosystem. To develop a deep understanding of these AI models and effectively communicate with them, it is necessary to understand their language. Therefore, in this article, we will develop an understanding of language models, how large language models work, what context is, and its importance in prompt writing.
If you haven’t been through our previous article, Here’s the link
What are Language Models?
Imagine a digital mind that gets human language. It can understand, interpret, and even makeup stories! This is what a language model really is. These AI wonders are getting smarter, doing things like writing poems or answering tricky questions. In this part, we’ll develop a basic understanding of Language Models. We have been interpreting with them a lot lately, from the voice commands of Alexa and Siri to text-based AI-like chatbots and automated customer service.
Fundamentally, a language model is a form of artificial intelligence, With the ability to comprehend, translate, and produce words in human languages. These models predict the next word or series of words in a given text by analysing large volumes of text data. Typically, machine learning techniques—particularly deep learning—are used to build language models because they enable the models to learn the relationships, patterns, and structures found in language.
Picture a digital librarian with A LOT of books. When you ask a question, it dives into its collection to find the best answer for you. But here’s the catch: a language model doesn’t grasp words like we do. Instead, it looks at patterns and connections between words to guess how to continue a sentence.
This technique, called autoregressive modelling, breaks down text into tiny pieces—like words or letters—and chooses the next piece based on what came before. It figures out these patterns by looking at tons of text data like books, articles, and more!
Language models play a crucial role in today’s artificial intelligence world, especially in Natural Language Processing (NLP). At their foundation, these models are complex statistical tools. They help us understand, create, and manage human language in written forms. With this technology, machines now interact with human language in exciting new ways. Applications range from chatbots and virtual assistants to advanced tools for text generation and analysis.
A key aim of a language model is to foresee the likelihood of word sequences. Simply put, when given a context or set of words, the model strives to predict what word should follow. This predictive skill is essential for many tasks, including text completion, translation, summarisation, and even creative writing.
These models are built on massive amounts of text data. This data is often collected from various resources such as books, articles, websites, and social media posts. Such a rich dataset lays the groundwork for how the model grasps language patterns, grammar rules, context details, and even some world knowledge.
The journey of language models has been filled with notable developments. Earlier versions were quite basic. They relied on n-grammes (which are groups of n words) and statistical chances. These models struggled to capture long-range relationships and subtle meanings in language. The rise of neural network-based models like recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks brought a huge leap forward for language modelling skills.
So, how do large Language models work?

- What are LLMs?
- Large Language Models, or LLMs, are advanced AI systems. They can understand and create human language. You can think of them as experts in language who predict, reply, and generate text accurately.
- Why are they “Large”?
- The term “large” refers to the huge amounts of data they learn from. We’re talking billions of words. They also have a staggering number of settings—parameters—that can reach into the trillions.
- Pattern Recognition Extraordinaire:
- At their essence, LLMs are very good at recognising patterns. Instead of just memorising data, they spot linguistic patterns and grammar rules. This is similar to how people learn language—through exposure and practice.
- Training:
- An Iterative Learning Process Training for LLMs involves going through a gigantic collection of text. Imagine a student reading through a whole library! They guess the next word in a sentence and adjust their settings based on how well they did. This process repeats billions of times. Over time, they improve their predictions to make coherent text.
- How Do They Generate Text?
- After they’re trained, LLMs respond by guessing one word—or token—at a time. Each new word adds context for the next one. This helps them create smooth and meaningful sentences.
- Creative and Unexpected Outputs:
- Unlike machines following strict scripts, LLMs generate responses based on chances. Because of this, they can come up with surprising or even creative answers. But sometimes, they may give plausible-sounding but wrong information—called “hallucinations.”
- The Power of “Attention”:
- One important feature of LLMs is something called an attention mechanism. When they create answers, they focus on key parts of the input text. This helps them keep long bits of conversation coherent and relevant.
- Task Versatility:
- Few-shot & Zero-shot Learning: LLMs can take on many tasks without needing special training for each one. If you ask them to translate or summarise text, they’ll pull from their extensive language knowledge to do it well. That’s why we call them “foundation models.”
- Broad Knowledge Base:
- Because they’ve been trained on mixed data sets, LLMs know about many subjects—from history and science to popular culture topics. However, use caution—although they seem knowledgeable, they don’t truly “understand” as people do. They work by matching patterns statistically rather than thinking consciously.
- Ethical Considerations:
- Even with all their abilities, LLMs face some big challenges too. For example, if the training data has a bias, it could also lead to biased outputs. Their enormous size needs lots of computer power, which raises environmental concerns too. Plus, like any powerful tool, there’s always a risk of misuse.
Now, let’s talk about some key players in the language model world!
Several big names in tech and research are leading the way in making these models. Here are some of the top ones:
- Open AI: Known for cool inventions like GPT-3 and GPT-4, OpenAI has done amazing things for natural language processing.
- Google AI: Google’s models like BERT and LaMDA are used everywhere—from helping search engines to chatting with users!
- Meta AI: You know Facebook? Meta has created models like OPT-175B and Galactica, focusing on social media and research.
- Microsoft: With Azure AI, Microsoft offers many models—for example, Megatron-Turing NLG—for developers to work with.
- DeepMind: This part of Alphabet has made models like Gopher and PaLM that look at general AI science.
- Hugging Face: Although it is not a model developer in the traditional sense, Hugging Face has become an important player in the AI language model ecosystem. They offer a platform where people can share and work together on machine learning models, including a lot of the most advanced language models.
What about types of Language Models?
They mainly fit into two groups:
- Generative Language Models: These can create high-quality, human-like text—whether for essays, translations, or creative work!
- Discriminative Language Models: These ones are all about specific tasks—like figuring out feelings in texts or summarising articles.
In short, language models are pretty cool! They’re changing how we interact with technology every day.
To Interact or use these language models, a good prompt needs to be communicated. Hence here are some
The concept of context and its importance in prompting
- Context in Language Models: Context is the surrounding information that adds meaning to text or prompts. It’s super important for making responses accurate.
Types of Context
- Internal context: This comes from what the model learnt during training. It includes facts and language patterns.
- External Context: This is the info given by users, like prompts, past messages, or extra data.
Importance of Context
- Disambiguation: It clears up different meanings. For example, “bank” can mean a riverbank or a financial institution.
- Specificity: It helps give precise responses tailored to what is asked.
- Tone and Style: Context affects whether the reply is formal or casual.
- Task framing: It defines what type of response is expected, like a summary or an analysis.
- Continuity: This ensures the conversation makes sense as it goes on.
- Personalisation: It customises output according to user likes.
Effective Prompting Strategies
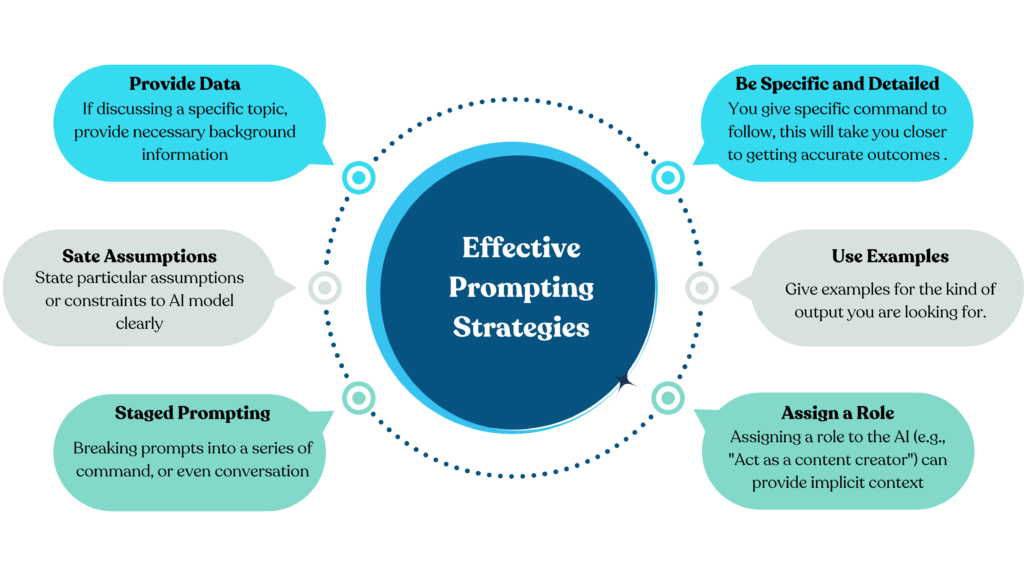
There are several good ways to add context to prompts.
- Be Specific and Detailed: Give clear, detailed instructions or background info. The more specific you are, the better the response will fit what you want.
- Use Examples: Show what kind of output you want with examples. This sets the stage and helps guide the model’s responses.
- Assign a Role to play: can help too. When you say something like, “Act as a history professor,” it gives clear context about what kind of knowledge and style you expect.
- Staged Prompting is another smart approach. Break complex tasks into smaller prompts, each one building off the last one. This helps keep the context flowing through your conversation.
- It’s also good to Explicitly State Assumptions. If there are specific things you want the model to consider, make sure to say them clearly!
- Provide Relevant Background when talking about a topic. Share important information to shape the conversation correctly.
Now, though language models do a great job with context, they still have some limits:
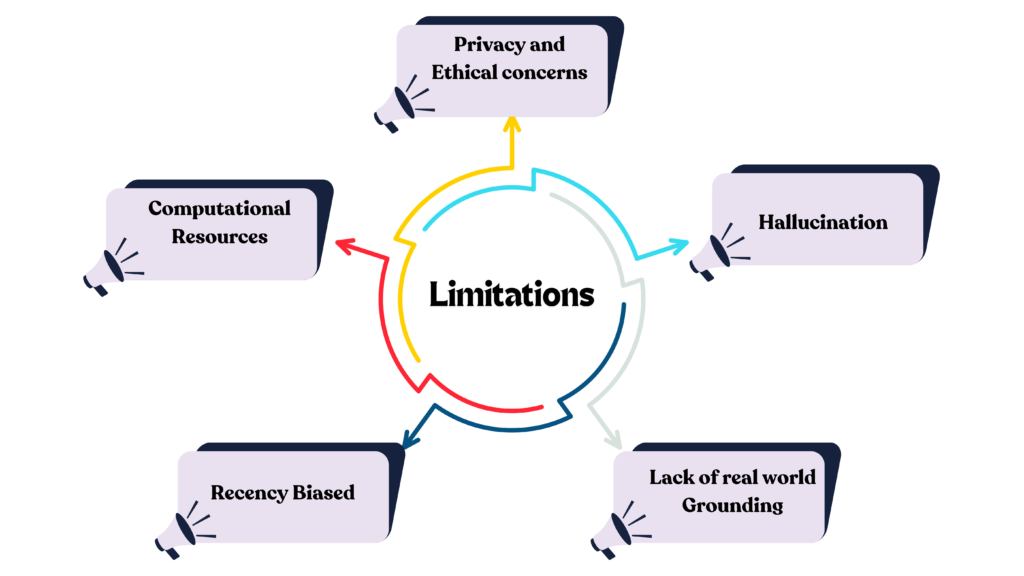
- Context Window is one of those limits. Models can only handle a certain amount of info at a time (this is called the context window). If your context is super long, it might cut off some important details.
- Recency Bias is another issue. Models often focus more on recent info, which can lead to missing out on crucial points that came up earlier in a long chat.
- Then there’s Hallucination. If your context is unclear or lacking, models might make up info that sounds right but isn’t actually correct.
- Also, remember that they lack Real-World Grounding. Their grasp on context comes from their training data—not from real-time events or personal experiences.
So how do we deal with these limits? Here are some best practices:
- First, prioritise important info. Put key context at the beginning of your prompt or chat so it grabs attention early on.
- Next is being Concise Yet Comprehensive. Share all necessary info, but keep it simple and avoid extras that don’t matter.
- Verify and Iterate if needed! If the model’s response doesn’t meet your needs, tweak your context and try again for better results.
- Using Explicit Markers can also help a lot. Clearly show different parts of your context (like “Background:”, “Question:”, “Constraints:”). This makes it easier for the model to sort through information.
- Finally, Maintain Consistency throughout the chat! Keeping things consistent prevents confusion for the model.
To wrap this up, understanding how to use context in prompting is key to getting the most from AI models. It leads to more precise and helpful interactions. As these models keep advancing, knowing how to provide and manage context will be super important for users wanting to get all they can from these tools—whether at work, in creative projects, or just chatting with AI assistants. Mastering this skill can make a big difference in improving the quality and usefulness of AI-generated content!
For more insightful AI content, Follow us on LinkedIn!