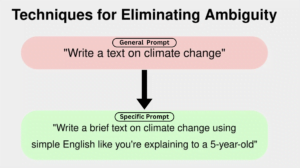
Bias in AI prompts can be intentional or unintentional and occurs when the input or phrasing of a question shows a particular assumption or perspective. These biases can be based on gender, race, culture, socio-economic status, or political preferences. To identify bias, evaluate the wording and test the results across different scenarios, genders, or cultural contexts. To address bias, use neutral phrasing, context-aware prompting, and ensure fairness, transparency, and inclusivity in every prompt. Ethical considerations should be a top priority in prompt engineering as AI systems have the power to shape decisions and affect people’s lives. Unethical prompts can perpetuate discrimination, spread misinformation, or result in harmful consequences. It also provides real-world examples and solutions to create better AI systems.